This is Lesson 12 of our Basic English Series.
Parts of Speech 2.3
Pronouns Part 3 – Personal Compound Pronoun
Compound pronouns are personal pronouns with the word self (singular) or selves (plural) are added to certain forms of the personal pronouns. Here are some examples of compound pronouns.
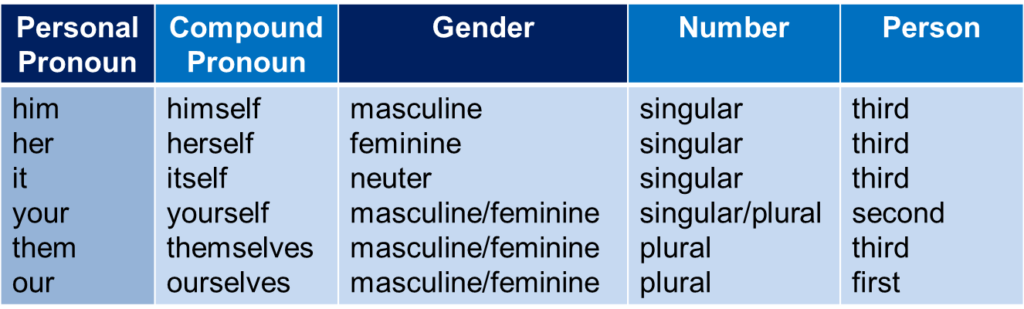
In connection with pronouns, here is rule number 17 in the English grammar.
ELGR17: Personal pronouns, including compound personal pronouns, must have an antecedent, and the number should also agree.
As discussed in Lesson 10, the antecedent is the noun for which a pronoun stands. However in this lesson, take note on the antecedents that were used in the examples, and this will be briefly explained at the conclusion of the lesson.
Here are some examples along with the errors in using personal compound pronouns.
Example 1:
– My friend Jim and myself appreciate your kindness. (Incorrect. The compound personal pronoun myself does not have an antecedent in the sentence.)
– My friend Jim and I appreciate your kindness. (Correct. The pronoun I was used as part of the compound subject. I is not a compound personal pronoun. In this case a compound personal pronoun is not needed.)
Example 2:
– He sent the documents to my friend and myself. (Incorrect. The compound personal pronoun myself has no antecedent.)
– He sent the documents to my friend and me. (Correct. The pronoun is located in the predicate and Me is the correct pronoun. In this case a compound personal pronoun is not needed.)
Example 3:
– They sent an invitation to the other team and ourselves. (Incorrect. The compound personal pronoun ourselves has no antecedent).
– They sent an invitation to the other team and us. (Correct. In this case a compound personal pronoun is not needed.)
Where and when to use compound personal pronouns
Now let us see the proper way of using compound personal pronouns.
Example 1 (Third person, plural)
The students did all these layouts themselves. (The personal compound pronoun themselves is correct because it has the antecedent students which is located in the subject of the sentence. The number, which is in the plural form, also agrees with the antecedent.)
Example 2 (First person, singular)
No one was around during the show so I had to do all the setup myself. (The personal compound pronoun myself is correct because it has the antecedent I which is located in the subject of the sentence. The number, which is in the singular form, also agrees with the antecedent.)
Example 3 (Third person, singular and feminine)
Courtney was the only one capable so she had to guide the others herself. (The personal compound pronoun herself is correct because it has the antecedents Courtney (noun) and she (pronoun) which are located in the compound subject of the sentence. The number and gender, which are in the singular form and feminine, also agree with the antecedent.)
Example 4 (Third person, singular and masculine)
No one was available to travel with Ricky so he did all the driving himself. (The personal compound pronoun himself is correct because it has the antecedents Ricky (noun) and he (pronoun) which are located in the compound subject of the sentence. The number and gender, which are in the singular form and masculine, also agree with the antecedent.)
Example 5 (Third person, plural)
No backup arrived to support the Alpha Team at the scene so they had to conduct all the operations themselves. (The personal compound pronoun themselves is correct because it has the antecedents Alpha Team (noun) and they (pronoun) which are located in the compound subject of the sentence. The number, which is in the plural form, also agrees with the antecedents.)
Example 6 (First person, plural)
We had to learn how to fly the plane ourselves as all our pilots were taken captives. (The personal compound pronoun ourselves is correct because it has the antecedents we (pronoun) which is located in the subject of the sentence. The number, which is in the plural form, also agrees with the antecedent.)
Example 7 (Third person, singular and neuter)
The ship’s sudden swing was so quick that the force was enough for it to return to its original position by itself. (The personal compound pronoun itself is correct because it has the antecedents ship (noun) and it (pronoun) which are located in the compound subject of the sentence. The number, which is in the singular form, also agrees with the antecedents.)
Take note of this once again: Antecedent of a compound pronoun can be a noun or a pronoun. In some cases both are present in the sentence and should agree with the compound pronoun that was used.
We have learned a the more complicated application of personal pronouns. We hope that this will guide you in improving your skills in this area.
In the next lesson we will cover another type of pronouns, the interrogative pronouns.
See you there.
Let us move on to the next lesson.
You may also jump to the lessons you want to see below.
