This is Lesson 16 of our Basic English Series.
Parts of Speech 2.7
Pronouns Part 6 (Continued) – The use of its as possessive pronoun
Some writers are confused between possessive pronouns and words where contraction was applied. In Lesson 15, ELGR19 states that: “Use the correct form of personal possessive pronouns and do not use an apostrophe to indicate ownership or possession…”. One example is the pronoun its, which is a neuter gender, third person possessive pronoun.
Let us use examples to help us understand this.
The team failed to achieve its goal. (Correct usage as pronoun)
Its goal was to win at all cost. (Partially correct. We will consider this later on the discussion about antecedents.)
The car’s performance did not meet its specifications. (Correct usage as pronoun)
It’s a lovely car, but did not meet its specifications. (The It’s is a contraction of the words It and is and its usage is correct being the subject in the sentence. The its is the car’s possessive pronoun referring to its specifications.)
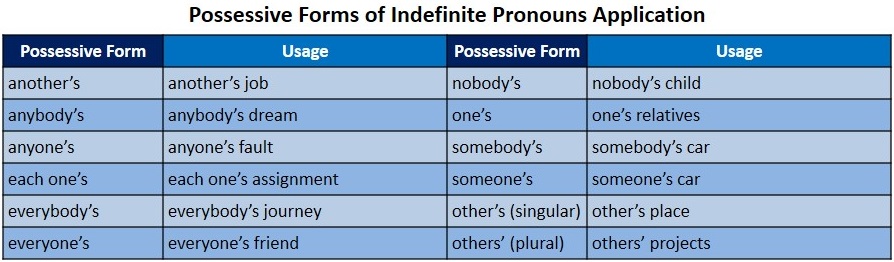
Pronouns Part 7 – Possessive Forms of Indefinite Pronouns
We have briefly covered indefinite pronouns in lesson 11 but here we will take a look at the English Language Grammar Rule number 20 (ELGR20) which will guide us in the correct usage of these pronouns.
ELGR20: Apostrophe (‘) and the letter s are needed to form the possessive of indefinite pronouns. However with the pronoun that end with the letter s such as others (plural), the apostrophe is added after the letter s without adding another s (others’).
Here was the definition of indefinite pronouns and some examples given in Lesson 11.
“Indefinite pronouns do not point out particular persons, places, or things. Some examples are another, both, all, some, many, more and each.”
Here are the possessive forms of these examples. We added more to help readers understand the ELGR20 above.

Let us use the above examples to familiarize ourselves with their correct use.
Pronoun Antecedent
In our previous lessons, we have mentioned and discussed about antecedents. We will consider this one more time in the use and application of pronouns. We have another grammar rule to keep in mind. It’s a short one but very important to remember.
ELGR21: A pronoun must agree with its antecedent as to person, number and gender.
ELGR21 explains antecedent in relation to the use of a pronoun, and it is the word that was previously used which that pronoun represents in the sentence. In most cases the antecedent is found in the subject of the sentence. It can also be in the preceding sentence. Let us go back to Lesson 10 where we started the topics on pronouns and take one of the examples.
Example using the same information in two scenarios:
1) Solomon was considered by many as among the wisest kings that existed in history, and he was also counted among the wealthiest rulers of the ancient world. Rulers of neighboring kingdoms respected him.
2) Solomon was considered by many as among the wisest kings that existed in history. He was also counted among the wealthiest rulers of the ancient world. Rulers of neighboring kingdoms respected him.
In the above example, the pronoun he and him were used to replace Solomon and agree with the antecedent which denotes the male gender.
Important to note: Some non-native English speakers have difficulty on this especially if their first language does not have distinction between the male and the female genders. Most noticeable, particularly in speaking, is the constant use of the male gender of pronouns even where the antecedents (Nouns) are female. Some even constantly use the pronoun he on common and neuter antecedents.
In Lesson 11 we covered three pronoun genders. But we will cover all four this time, and these are the masculine, the feminine, the common and the neuter genders . Here they are below along with some examples:
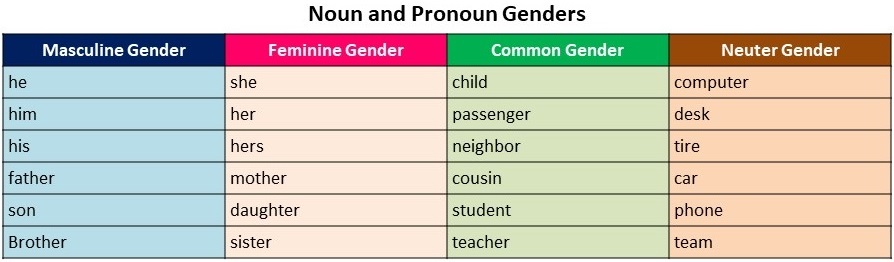
Nouns and pronouns as discussed in previous lessons have also numbers and these are the singular and plural numbers. These also should be kept in mind as to which form to use in relation to the antecedent. Here are some examples:

Examples on proper use of antecedents:
- Everyone entering the auditorium had to present his personal identification.
(In this example, his is a singular pronoun that is of the same form as the antecedent everyone.) - Only few of the students came in their proper uniforms.
(Few is the antecedent of their and both agree in number which is in the plural form) - The commander did not know how to deal with the situation himself.
(The word commander is the antecedent for the pronoun himself and they agree in number which is singular in form.)
This particular lesson may seem tough but constant practice can help. The next one will still deal with the antecedent with the more tricky aspect where errors are commonly noticeable among non-native English speakers.
See you in the next lesson.
You may also jump to the lessons you want to see below.
